Leave Your Message
The Phase Of Transformer is crucial in electrical systems. Understanding its significance can greatly enhance efficiency and performance. Dr. Emily Johnson, an expert in power systems, stated, "The phase configuration of a transformer determines how effectively it interacts with the grid." This highlights the vital role phases play in electrical engineering.
Transformers operate in various phases, impacting voltage and current levels. Incorrect phase alignment can lead to inefficiencies. Many engineers overlook this aspect, risking operational failures. In real-world applications, the choice of phase can influence everything from energy loss to equipment lifespan.
Moreover, the Phase Of Transformer affects the overall stability of the electrical network. An imbalance can disrupt the entire system. This complexity necessitates careful planning and execution. Engineers must pay close attention to phase relationships. Each decision shapes the performance of entire electrical grids.

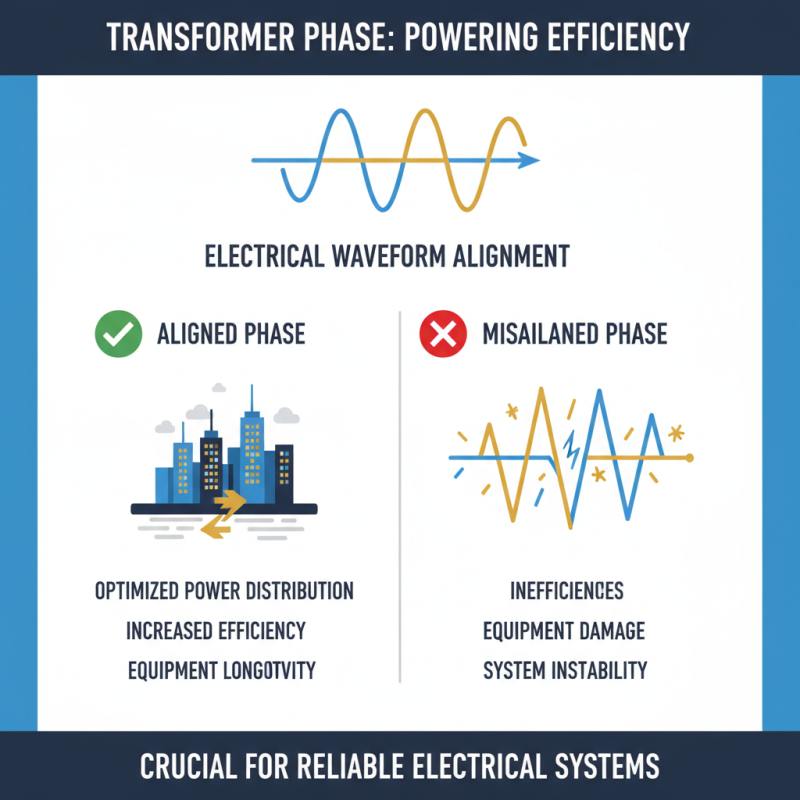
The phase of a transformer plays a crucial role in electrical systems. It refers to the alignment of the electrical waveforms. Understanding transformer phase is essential for optimizing power distribution. A misalignment can lead to inefficiencies and potential equipment damage.
In an electrical system, transformers often operate in a multi-phase arrangement. This multi-phase setup can improve power delivery. According to industry reports, three-phase systems are commonly used due to their ability to deliver power more efficiently. They reduce the amount of copper required for wiring by up to 25%. However, incorrect phasing can lead to unbalanced loads and overheating.
Moreover, the phase relationship affects power quality. Voltage fluctuations may occur if phases are not synchronized correctly. Studies indicate that unresolved phase issues can result in a 15% increase in operational costs. Ensuring proper phase alignment in transformers is not just advisable—it is necessary for reliable performance. The challenges in real-world applications often highlight this need for careful phase management.
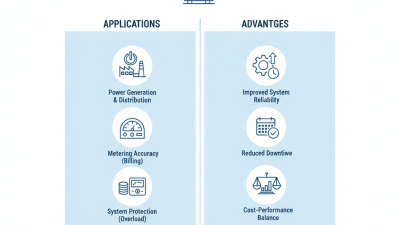
Transformers play a crucial role in electrical systems. Understanding transformer phases is essential for efficient operations. There are primarily three types of transformer phases: single-phase, two-phase, and three-phase configurations. Each type has unique characteristics that influence its applications.
Single-phase transformers are commonly used in residential settings. They handle lower power loads effectively. Operating with two wires, they are simpler and cheaper. However, they are not as efficient for high power requirements. Approximately 85% of homes rely on these transformers for their electrical needs.
On the other hand, three-phase transformers are prevalent in industrial applications. They provide a steady power supply and are more efficient. These transformers use three separate windings and can transmit higher voltages. They account for nearly 90% of the global transformer market due to their reliability and efficiency. Investing in the right phase type can make a substantial difference in energy use and costs. Selecting the correct transformer phase is vital for minimizing energy losses and ensuring that systems run smoothly.
The phase of a transformer plays a critical role in power distribution efficiency. In electrical systems, the phase determines how voltage and current interact across transformers. Proper phase alignment ensures optimal energy transfer. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, unbalanced phases can lead to energy losses of up to 20% in certain systems. This inefficiency can be costly for both utilities and consumers.
Transformers operate in three-phase systems. Each phase should align for seamless energy distribution. Misalignment can result in equipment overheating and reduced lifespan. Studies indicate that incorrect phase connections account for 10% of transformer failures. Addressing these issues requires ongoing monitoring and testing. Such action helps prevent larger disruptions in the electrical grid.
However, many installations overlook phase management. Operators may assume all phases function correctly without validation. Without periodic checks, these systems can unknowingly operate below their potential. Inconsistent phase connections not only disrupt power flow but can also escalate operational expenses. Identifying and rectifying phase mismatches is essential for improving overall efficiency.
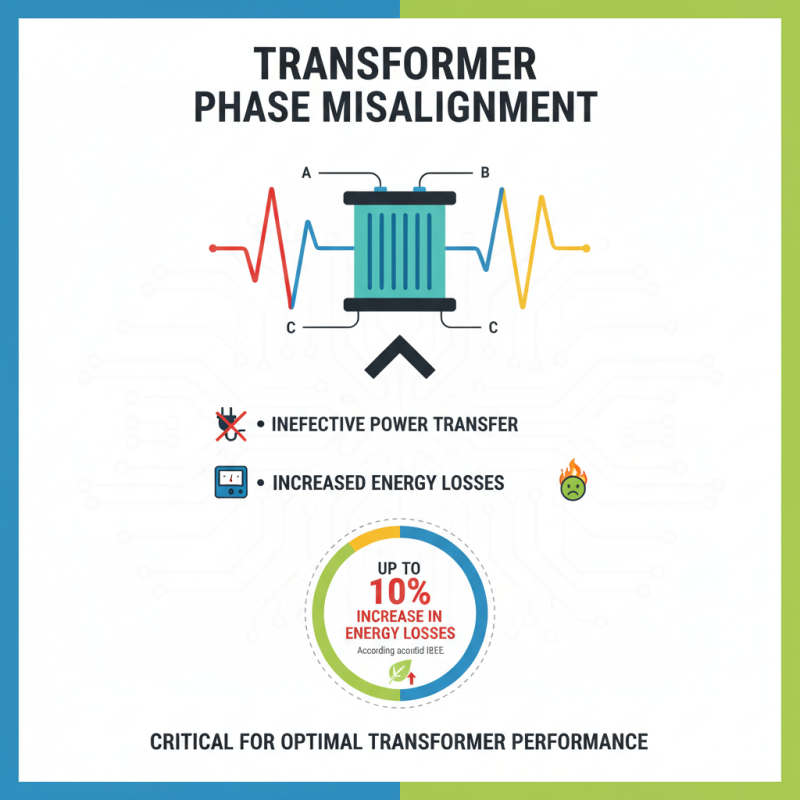
Phase misalignment in transformers can significantly affect performance. It occurs when the voltage or current waveforms are not synchronized. This can lead to ineffective power transfer and increased losses. According to the IEEE, phase misalignment can cause up to a 10% rise in energy losses. This emphasizes the critical nature of transformer phases.
In real-world applications, phase misalignment can lead to overheating. A study reported that 30% of industrial electrical systems experience overheating due to phase issues. This not only reduces equipment lifespan but can also lead to system failures. Heat accumulates, causing insulation breakdown and equipment damage. In addition, proper phase alignment is crucial for maintaining load balance, preventing overloads on transformers.
Monitoring and adjusting phase alignment can enhance electrical performance. Studies suggest that regular assessments can reduce operational costs by 15%. Despite the available data, many systems remain unmonitored. This lack of attention presents risks that could be avoided through proactive measures. Ultimately, addressing phase misalignment in transformers is vital for efficient energy use and system reliability.
Proper phase management is crucial in electrical design. Each phase of a transformer plays a vital role in distributing electrical power efficiently. A well-balanced phase system reduces losses and improves overall system performance. If one phase is overloaded, issues can arise, such as equipment failure or voltage fluctuations.
In practice, engineers often face challenges managing phases correctly. Incorrect phase arrangement can lead to unbalanced loads. This situation can cause overheating and ultimately shorten the lifespan of electrical components. Tracking and adjusting these phases can be time-consuming. Yet, this effort is essential for reliability.
Awareness of phase importance should be a priority for designers. Simple mistakes, like mislabeling phases, can lead to significant consequences. Regular checks and proper documentation help maintain phase integrity. Emphasizing a meticulous approach in design processes leads to more resilient electrical systems. Making phase management a central focus is necessary for safe operations.
| Phase Type | Description | Importance | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Phase | Electrical power is supplied through a single alternating current (AC) conductor. | Simpler design, ideal for low power devices and residential applications. | Household appliances, lighting systems. |
| Three-Phase | Electromotive force is delivered via three conductors, each 120 degrees out of phase. | More efficient for transmission, reduces power loss over long distances. | Industrial motors, transformers, and large HVAC systems. |
| Polyphase | Involves multiple phases (more than three) in electrical systems, commonly used in specialized applications. | Increases efficiency in certain applications, allows for larger loads. | High-powered industrial systems, data centers. |