Leave Your Message
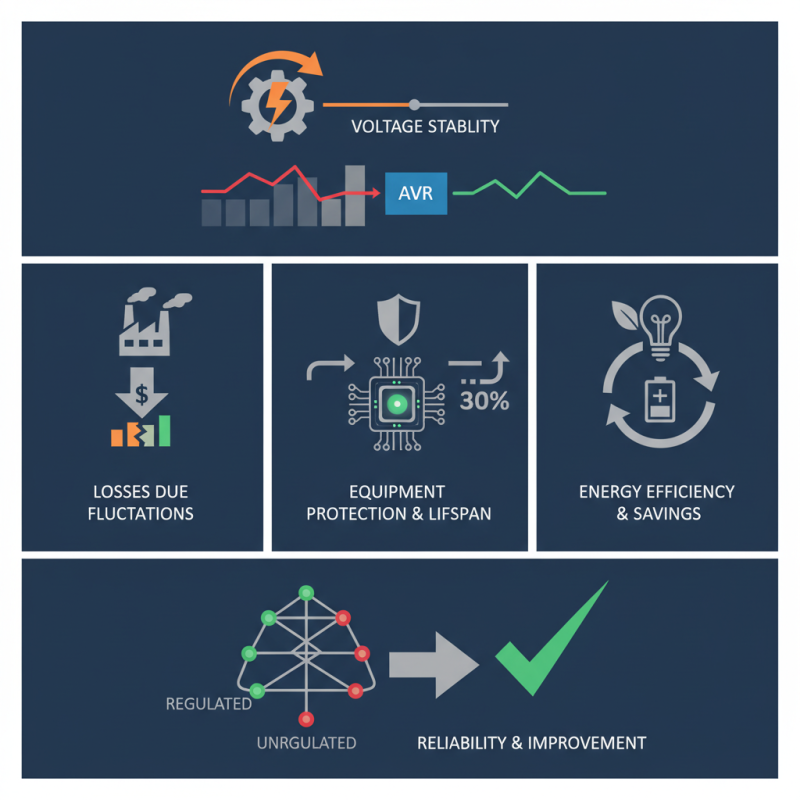
An Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR) is crucial for maintaining electrical system stability. It ensures that voltage levels are consistent and protects sensitive equipment. According to the IEEE, voltage fluctuations can lead to significant losses in industrial settings. The damage caused by these fluctuations can reach up to $1 billion annually for companies.
AVRs work by automatically adjusting the voltage output to match the load requirements. This capability is essential for industries relying on continuous power supply, such as manufacturing. Overloading or underloading can result in equipment failure, leading to additional costs. In fact, studies show that improper voltage regulation can reduce the lifespan of electrical devices by 30%.
In an era where energy efficiency is paramount, the AVR stands out. It directs energy more effectively, reducing wastage. However, some systems still operate without adequate regulation, highlighting the need for improvement. Embracing AVRs is not just about compliance; it’s about ensuring long-term reliability and energy savings in the electrical grid.
An automatic voltage regulator (AVR) is crucial for maintaining the stability of electrical systems. It ensures that voltage levels remain consistent, preventing fluctuations that can damage equipment. According to industry reports, proper voltage regulation can extend the life of electrical devices by up to 30%. For sensitive machinery, even small voltage deviations can lead to significant operational issues.
Tips: Regular maintenance of AVRs can help identify potential problems early. Keep an eye on voltage readings to catch any irregularities.
Understanding how AVRs function is key. They monitor output voltage and make adjustments as needed. This adaptability is vital in industries where heavy machinery is used. For instance, in manufacturing, a sudden power surge can lead to errors or machine failures. In fact, it’s reported that voltage irregularities are responsible for 60% of equipment malfunctions.
Tips: Consider investing in advanced monitoring systems for your AVRs. It provides real-time data that can prevent costly downtime. Make sure your team is trained to recognize warning signs related to voltage regulation.
Voltage stabilization is crucial for the reliable operation of electrical systems. Fluctuating voltage levels can lead to equipment damage, operational inefficiencies, and safety hazards. An automatic voltage regulator (AVR) helps maintain consistent voltage. It reacts to changes in electrical load and adjusts output accordingly.
Consider a manufacturing plant. Machines there require a stable voltage to function effectively. If the voltage dips too low, motors may stall or malfunction. Over time, this can lead to costly repairs. On the other hand, high voltage can cause overheating and damage sensitive components. With proper voltage regulation, these risks diminish significantly.
In residential setups, voltage fluctuations can disrupt daily life. Electronics can be sensitive to changes in power supply. An AVR helps protect such devices from unexpected spikes. In the end, understanding the importance of voltage stabilization can help prioritize safety and efficiency in electrical systems. It's a detail that should not be overlooked.
An Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR) plays a crucial role in electrical systems. It ensures stable voltage levels, protecting sensitive equipment. Voltage fluctuations can harm machinery, leading to costly repairs. The AVR continuously monitors voltage levels and makes real-time adjustments. This feature helps maintain a steady electrical supply.
Tips: Regularly checking the AVR can prevent issues. Look for signs of wear or irregular voltage readings. Early detection is key.
Another key function of the AVR is to improve energy efficiency. By regulating voltage, it reduces wastage. High voltage can lead to overheating and energy loss. An AVR optimizes power usage, saving money and enhancing performance.
Tips: Consider using a more advanced AVR for complex systems. Evaluate the load requirements regularly. Matching the AVR to the system's needs is essential for optimal results.
| Function | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Regulation | Maintains the output voltage within a specified range | Ensures the stability and reliability of electrical equipment |
| Load Balancing | Distributes electrical load evenly across the system | Prevents overloads and improves the lifespan of components |
| Protection from Voltage Spikes | Cuts off excess voltage to avoid damage | Safeguards sensitive equipment from damage |
| Transient Response | Quickly adjusts to sudden changes in load | Maintains stable operation under variable conditions |
| Efficiency Improvement | Reduces energy losses by optimizing voltage levels | Contributes to lower operational costs |
Voltage fluctuations can cause significant issues for electrical equipment. Devices designed to operate within specific voltage ranges may fail if these levels are not maintained. For instance, an appliance rated for 230 volts might struggle when the voltage drops to 180 volts or spikes to 250 volts. This can lead to premature wear, damage, or even complete failure.
Consider a small factory with various machines. If those machines experience inconsistent voltage, their performance can suffer. Motors may overheat or underperform when voltage levels fluctuate. This not only affects productivity but can also lead to expensive repairs. In some cases, sensitive electronics may be irreparably damaged by sudden spikes.
The importance of having an automatic voltage regulator becomes clear in this scenario. It minimizes risk by ensuring a stable power supply. Without it, the potential for disruption is high. However, not every system is equipped with such safeguards. This oversight can result in costly consequences, showcasing a gap in many electrical systems' designs. Recognizing these dangers allows for better planning and investment in voltage regulation solutions.
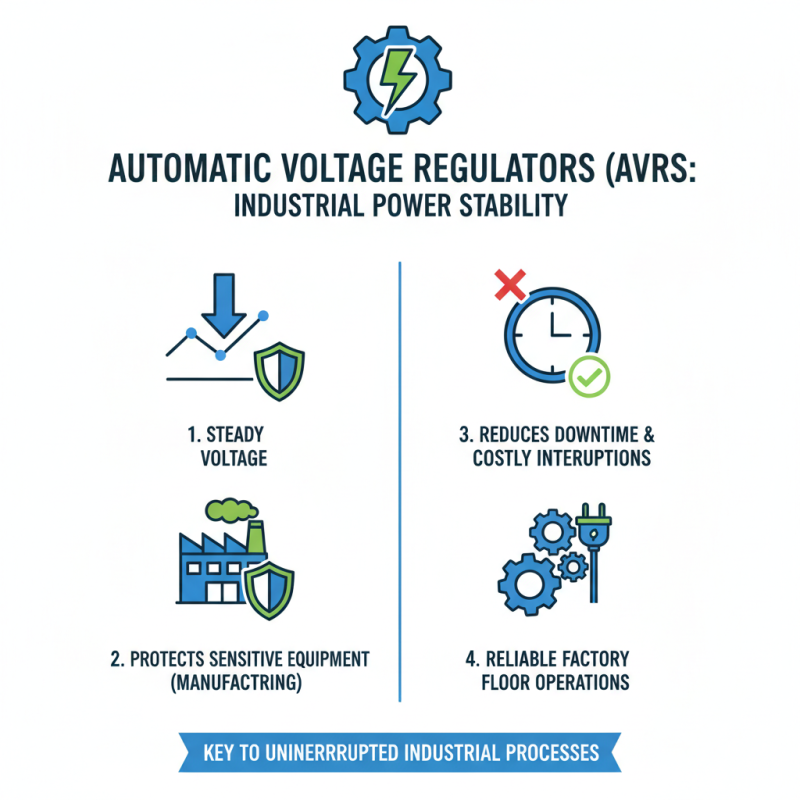
Automatic voltage regulators (AVRs) play a vital role in various industries. They maintain a steady voltage level, ensuring that machines operate smoothly. In manufacturing, for instance, AVRs protect sensitive equipment from voltage fluctuations. This helps reduce downtime, which can be costly. Factory floors rely heavily on consistent power.
In the telecommunications sector, AVRs stabilize voltage for servers and communication devices. Any disruption can lead to data loss or service interruptions. Keeping systems running efficiently is essential. Hospitals also benefit from AVRs. They ensure that critical medical equipment functions without interruptions.
However, not all facilities invest in AVRs. Some overlook their importance, risking equipment and safety. This choice can lead to failures that might be avoided. Organizations should evaluate their power needs and reconsider their voltage management strategies. Investing in AVRs could enhance reliability and performance significantly.